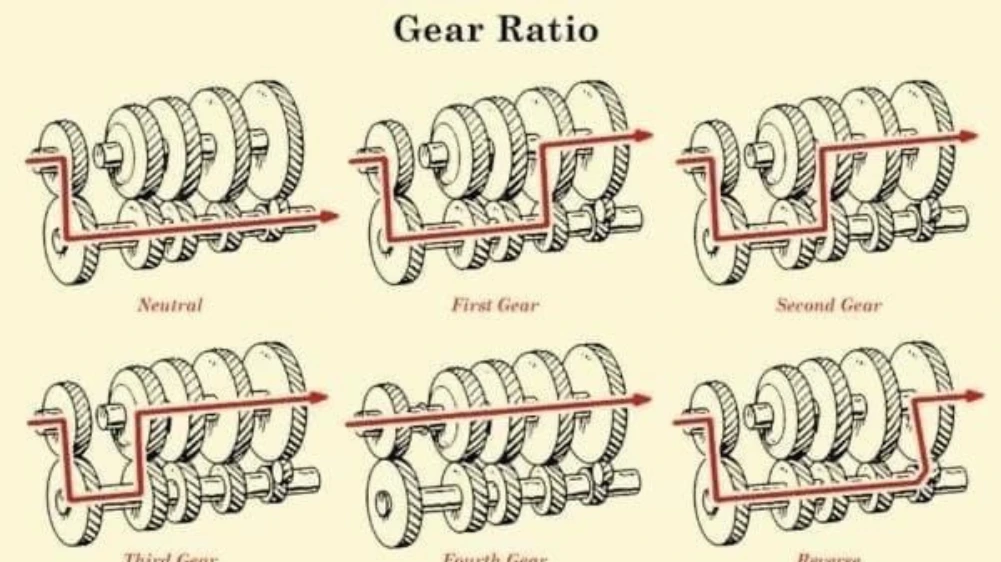
The world of automotive engineering has seen dramatic transformations in the past few decades. Among these innovations, the Automated Manual Transmission (AMT) stands out as a unique blend of manual control and automatic convenience. It promises fuel efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and driving comfort — all rolled into one system.
In this in-depth guide, we’ll explore how an automated manual transmission works, how it compares to other transmission types, and why it’s becoming increasingly popular in modern vehicles.
What is an Automated Manual Transmission?
An Automated Manual Transmission is a hybrid system that combines the components of a traditional manual gearbox with an electronic control system to automate gear shifts. Unlike fully automatic transmissions, it retains the internal gear structure of a manual transmission but eliminates the need for a clutch pedal or manual gear shifting by the driver.
In simple terms:
It’s a manual transmission with automatic gear-shifting capabilities.
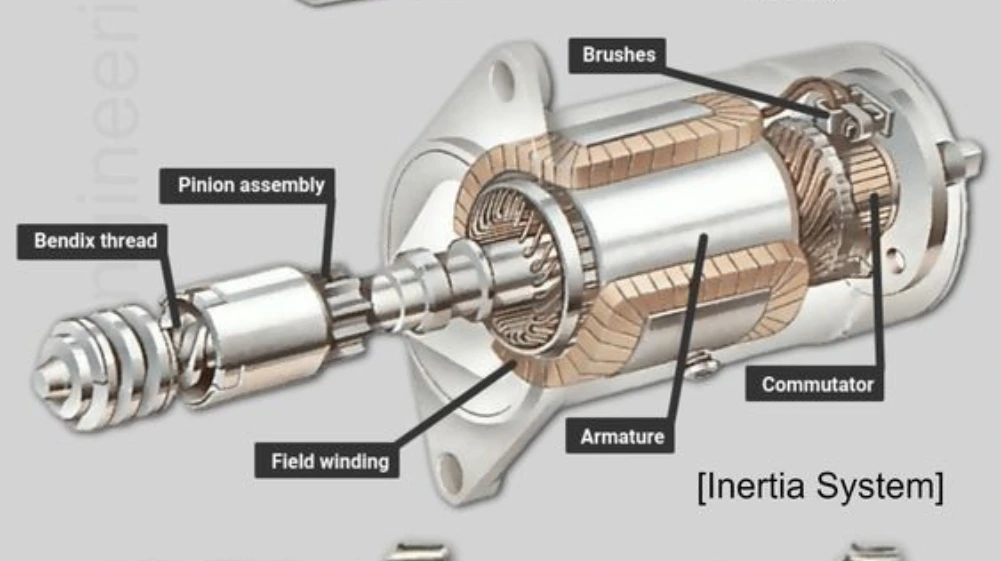
Key Components of an Automated Manual Transmission
To understand how this system works, it’s important to know the main components involved:
1. Manual Gearbox
The core mechanical part remains a standard manual transmission with gears and gear selectors. This helps keep costs and weight low while maintaining high mechanical efficiency.
2. Actuators
These are electromechanical devices that take care of clutch operation and gear selection. They replace the human foot and hand that traditionally handle the clutch and gear lever.
3. Transmission Control Unit (TCU)
This is the brain of the system. It uses sensors and algorithms to determine when and how to shift gears. It processes information such as engine speed, throttle position, and vehicle load to make shifting decisions.
4. Sensors
Various sensors monitor speed, RPM, throttle input, and other driving conditions. These signals are sent to the TCU to help it determine the optimal gear at any given moment.
How Does an Automated Manual Transmission Work?
Let’s break down the process of how an automated manual transmission functions step-by-step:
Step 1: Start-up
When you start the vehicle and press the accelerator, the TCU activates. It engages the first gear automatically through the clutch actuator.
Step 2: Clutch Engagement
The system uses sensors to determine when to engage or disengage the clutch. The clutch actuator mimics the action of a human foot on the pedal, allowing smooth transitions.
Step 3: Gear Shifting
As you drive and increase speed, the TCU calculates the ideal time to shift gears based on real-time inputs. Once the shift point is reached, it commands the gear actuator to move the selector forks and engage the next gear.
Step 4: Downshifting
When you decelerate or slow down, the system performs automatic downshifting. It may also engage engine braking depending on driving mode and slope.
Step 5: Stop & Hold
At traffic signals or stop conditions, the clutch is automatically disengaged. Some AMT systems come with “creep mode,” where the car slowly rolls forward when you release the brake, just like in automatic vehicles.
Modes of Operation in AMT
Most modern automated manual transmission systems offer dual modes for flexibility:
- Automatic Mode: Fully automated — the TCU handles everything.
- Manual Mode (Tiptronic or Paddle Shift): The driver can manually select gears using buttons, paddles, or the gear lever (but still without a clutch pedal).
This dual-mode flexibility is a key reason for AMT’s rising popularity in both passenger cars and commercial vehicles.
Advantages of Automated Manual Transmission
Here are some of the top benefits of using an automated manual transmission in modern vehicles:
Fuel Efficiency
Because it’s based on a manual gearbox, AMT systems often deliver better fuel economy than traditional automatic transmissions.
Lower Cost
An AMT is cheaper to manufacture and install compared to CVTs or dual-clutch transmissions. It’s a cost-effective upgrade from a manual setup.
Easier to Drive
No clutch pedal means reduced driver fatigue in city traffic. Even beginners find AMT vehicles easier to handle.
Low Maintenance
Fewer moving parts and mechanical simplicity make AMT systems easier and cheaper to maintain than fully automatic transmissions.
Lightweight
Unlike traditional automatics with torque converters, AMTs are lighter, which contributes to better mileage.
Disadvantages of Automated Manual Transmission
Despite the advantages, there are a few downsides as well:
Shift Lag
One common complaint is a slight delay or jerk during gear changes, especially in older or low-cost AMT systems.
Not for Performance Enthusiasts
AMTs are designed for fuel efficiency and ease of use, not sporty performance. Enthusiasts often find the response less engaging.
Hill Assist May Be Absent
Some basic AMT models don’t include hill-hold features, making starts on inclines trickier.
Automated Manual Transmission vs. Other Transmission Types
| Feature | AMT | Manual Transmission | Automatic (Torque Converter) | CVT | DCT |
| Clutch Pedal | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| Fuel Efficiency | High | Highest | Medium | High | High |
| Driving Comfort | High | Low | Very High | Very High | Very High |
| Maintenance Cost | Low | Low | High | Medium | High |
| Shift Lag | Medium (in budget models) | None | Low | Low | Very Low |
| Cost | Low | Lowest | High | Medium | High |
Where is AMT Commonly Used?
- Passenger Cars: Many entry-level and mid-range cars from brands like Maruti Suzuki, Tata, Renault, and Hyundai now come with AMT variants.
- Commercial Vehicles: AMT is also popular in light commercial vehicles and city buses due to reduced driver fatigue and improved fuel efficiency.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Some electric models use single-speed versions of AMT for cost and simplicity.
Future of Automated Manual Transmission
As technology advances, AMT systems are becoming smoother, more intelligent, and more responsive. Many modern AMT-equipped cars now include AI-driven learning, where the TCU adapts to the driver’s habits to improve shift logic.
With continued innovation, automated manual transmission may remain a key part of the drivetrain evolution, especially in markets focused on affordability and efficiency.
Considering a new car? Don’t overlook models with an automated manual transmission. They may surprise you with their efficiency, comfort, and value. Share this article with anyone exploring transmission options!
Conclusion:
The automated manual transmission is a smart fusion of manual mechanics and electronic control. It offers an excellent balance between cost, efficiency, and ease of use. For everyday driving, especially in urban environments, it removes the hassle of gear shifting while maintaining fuel economy.
Although it may not yet match the ultra-smoothness of advanced automatics or the thrill of a pure manual, AMT continues to improve with each generation. For many drivers, it represents the best of both worlds.